- Insurance coverage among young adults aged 19 to 26 has trended upward since the extension of dependent care coverage by the Affordable Care Act.
- Mental health service utilization has shown a similar upward trend, with more young adults reporting that they are receiving mental health treatment.
- Since the dependent care expansion, overall substance use treatment remains level while fewer uninsured young adults report receiving substance use treatment.
- Cost barriers associated with mental health service or substance use treatment have fallen in the wake of the dependent care expansion.
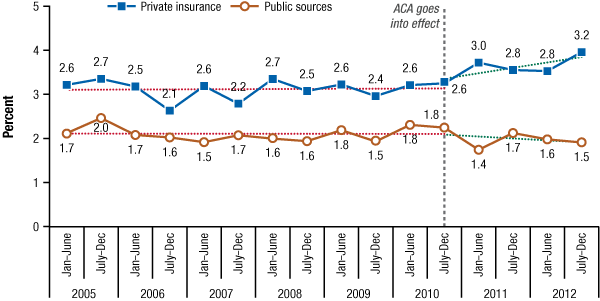
- Payment for treatment has shifted away from public sources, with private insurance becoming a more prevalent source of payment.
In September of 2010, the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act (ACA) extended dependent care coverage to young adults, allowing individuals under the age of 26 to remain on their parents’ insurance regardless of educational, employment, or marital status. Prior to the ACA, individuals were typically dropped from their parents’ insurance on their 19th birthday or upon their graduation from high school.1 As a result, the cohort aged 19 to 26 suffered from the highest rates of uninsurance, with approximately 30 percent of these individuals lacking coverage in the years before the ACA was enacted.2 Increasing insurance coverage among these individuals became a policy priority because lack of insurance coverage is associated with a number of adverse outcomes, including lower health care utilization rates and delay of care that often exacerbates medical conditions.3,4,5
This short report highlights the trends in mental health and substance use treatment service use by young adults aged 19 to 26 before and after the dependent care coverage extension. Examining the trends in coverage and utilization gives insight into the impact of the ACA’s dependent care coverage expansion. The results are estimates from the National Survey on Drug Use and Health (NSDUH) from 2005 to 2012.6 NSDUH, conducted by the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration’s (SAMHSA’s) Center for Behavioral Health Statistics and Quality (CBHSQ), is a survey of the civilian, noninstitutionalized U.S. population that covers a wide range of issues, including insurance coverage and use of mental health and substance use treatment services. Standard statistical t-tests of means accounting for NSDUH’s complex survey design have been conducted for all statements appearing in the text that compares estimates between years. Unless otherwise noted, all statements that describe differences are significant at the .05 level.